How Can Continuing Education Support Students Across Their Learning Lifecycle?
Continuing education has evolved from professional development to lifelong learning support that institutions must prioritize to remain competitive.
- Skills obsolescence is driving unprecedented demand for career transition programs and skills-based training.
- Hybrid continuing education models have grown, even as total higher education enrollment declined.
- Online learning platforms now enable personalized, flexible delivery that accommodates working professionals' complex schedules and career advancement needs.
- Leading institutions are demonstrating measurable success through technology-enabled student lifecycle management.
Institutions that implement comprehensive continuing education support across the entire student lifecycle will capture the expanding lifelong learning market.
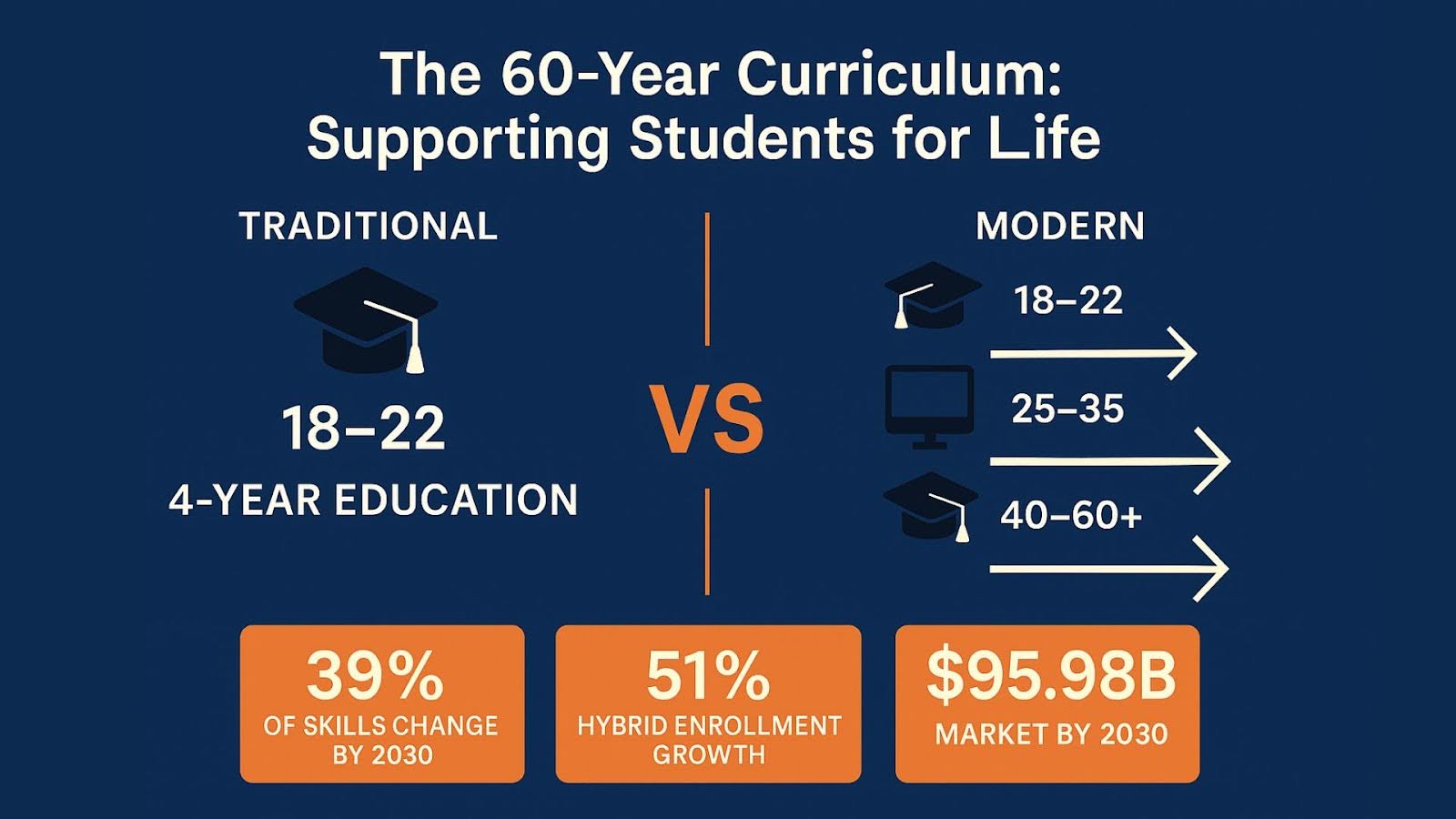
Higher education has undergone a transformation that surpasses traditional degree programs. The target demographic is no longer exclusively 18- to 22-year-olds fresh out of high school. Today, an increasing number of adult learners are enrolling in postsecondary programming, attempting to reskill and acquire new knowledge as technology has altered their basic job requirements.
Employers expect that 39% of key job skills will change by 2030. This accelerating pace of skills obsolescence means workers face not just changing jobs requiring new skill sets but multiple careers as some occupations disappear and others emerge seemingly overnight. Understanding how continuing education supports students is imperative to keep up with this reality.
Learner expectations have changed too. Students want to invest their time and resources with education providers who understand their priorities and can support them in their learning journeys as they seek to develop valuable and future-ready skills. The competition for adult enrollments now includes universities, MOOCs, private providers and employers all vying for the same learners.
How Has Lifelong Learning Changed How Continuing Education Supports Students?
The rise of the "60-year curriculum" model explains how modern institutions think about education delivery. Unlike the traditional three-stage life pattern of education, work and retirement, people now live longer and must continuously update their skills to remain relevant in the workforce.
This transformation has created unprecedented demand for career transition programs and skills-based training. The U.S. continuing education market, valued at $66.91 billion in 2024, is projected to reach $95.98 billion by 2030, driven largely by the need for continuous skill development.

Online learning platforms have been instrumental in ensuring continuing education supports students with accessibility. Hybrid enrollment grew by 51% between fall 2017 and 2023, even as total higher education enrollment declined 3% during the same period. This growth reflects evolving student demand for flexible learning options that accommodate work and family commitments.
Modern continuing education programs now focus heavily on micro-credentials, certificate programs and competency-based learning pathways. These shorter, targeted programs allow working professionals to gain specific skills without committing to full degree programs. The emphasis has shifted from theoretical knowledge to practical, immediately applicable skills that address real workforce needs.
What is the Student Lifecycle (and How Can You Make the Most of It)?
One way to capitalize on the lifelong learning opportunity and thrive is to adapt to delivering education across the modern student lifecycle.
Traditionally, the student lifecycle was fixed over a short term. Institutions recruited students out of high schools, delivered necessary financial aid, supported their persistence and degree completion and then engaged them as alumni to generate donations.
In the modern education market, the lifecycle has changed. Universities can no longer rely on a short education engagement followed by a long-term donation-based relationship. Instead, successful institutions must continue delivering meaningful and contextual programming to learners throughout their lifetime, supporting them through multiple career transitions and skill updates.
The modern student lifecycle mirrors the customer lifecycle, requiring institutions to think strategically about long-term relationships rather than transactional interactions. Below, we explore the stages of this evolved lifecycle and share strategies for creating lasting educational partnerships.
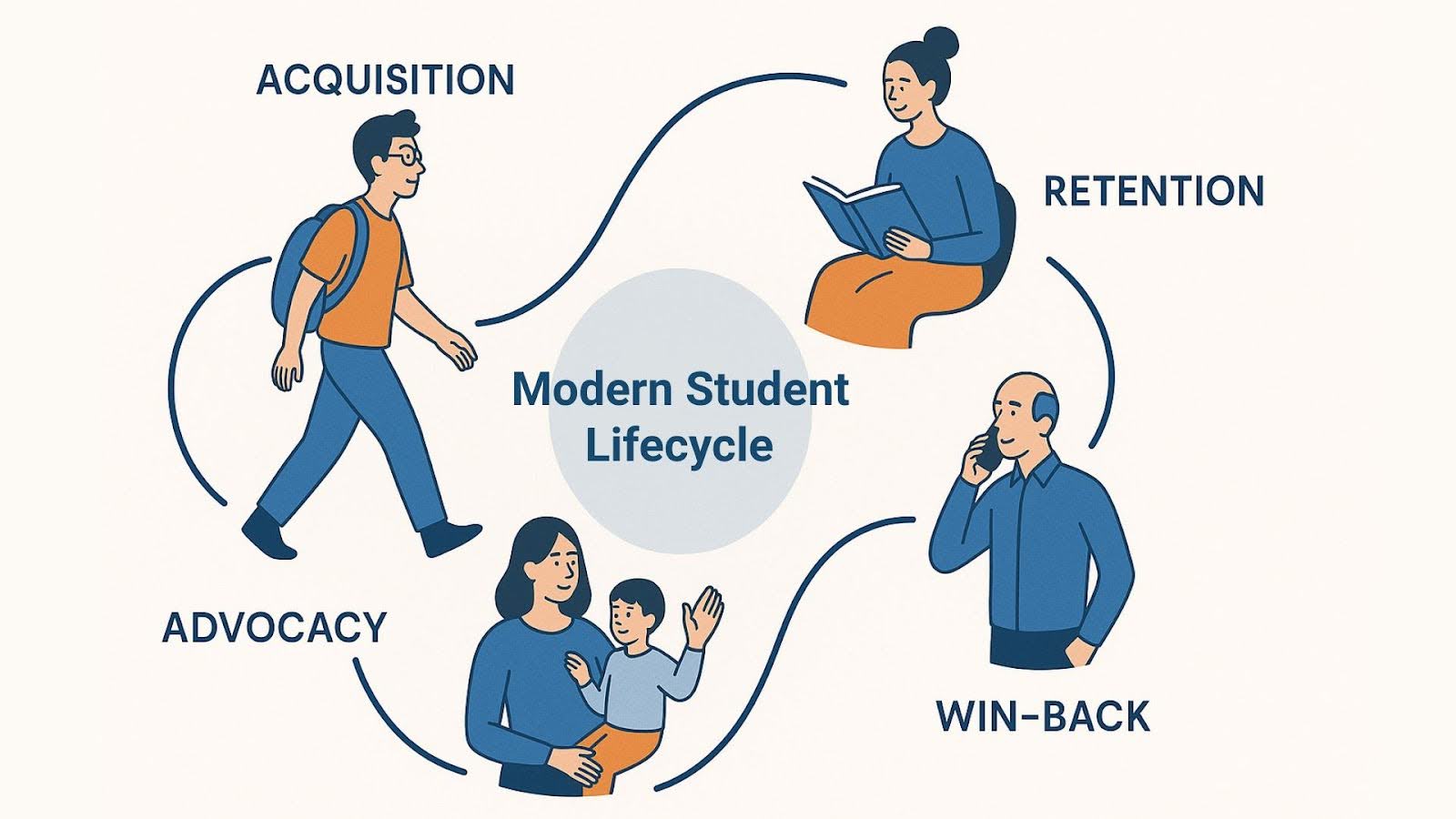
1. Acquisition (Bring Learners in the Door)
Learners have numerous programming options to choose from, making acquisition more competitive than ever. While curriculum quality remains a major differentiator, other factors influence students' decision-making processes. Speed to market has become crucial. How quickly can you modify course content to address particular employer and student needs and launch market-responsive programs?
Successful institutions prioritize the student experience by ensuring learners have access to up-to-date and accurate information before making program choices. This support requires intelligence around learner preferences and desired outcomes to push targeted campaigns that generate interest and bring students through the door.
Career transition programs have become particularly effective for acquisition. These programs target professionals seeking to pivot into new fields, offering clear pathways from their current expertise to emerging opportunities. Skills-based training modules that address immediate workplace needs also attract learners looking for quick, applicable solutions.
Once you have each student's attention, you need a simple and effective registration process that helps them enroll in just a few clicks. Modern online learning platforms have streamlined these processes, making it as easy to enroll in a continuing education course as it is to purchase any other digital service.
2. Retention (Keep Learners Satisfied and Content)
Once students are enrolled, you need to keep them happy and satisfied throughout their learning experience. Learners have taken time out of their busy schedules to gain new skills. This precious time must be spent on education alone, not managing administrative tasks like requesting transcripts or payment receipts.
Self-service portals that allow learners to manage most administrative tasks themselves make students self-sufficient while enhancing their lifelong learning experience. Hybrid continuing education models have proven effective for retention, as they offer the flexibility of online learning combined with the engagement of in-person interaction.
The most successful programs incorporate interactive features like discussion forums, real-time feedback and competency-based assessments. Incorporating interactive features can boost learner engagement by 25% and improve knowledge retention by 15%.
3. Win-Back (Enable Learners to Keep Coming Back for More)
Learners operate in an open marketplace without particular ties to one institution over another, especially for non-credit offerings. Even credit-bearing students can easily transfer credits, creating low barriers for exit and re-entry elsewhere.
These "swirling" students seek the most economical means to meet their learning needs. To serve them effectively, institutions need personalized marketing that educates learners about new courses and offerings relevant to their experience as programming becomes available. Information about past enrollments, interests, goals and career outcomes should inform strategies to win learners back.
Career advising plays an important role here as well. Current students and alumni need to see that institutions are committed to their success by showing them pathways that can help them accomplish their goals or support their learning needs through different life and career stages.
4. Advocacy (Make Learners Your Promoters)
Past learners can become the most powerful advocates for continuing education programs. However, institutions need to keep them engaged well beyond course completion so they keep returning and act as references as enrollment grows.
Digital credentials provide an excellent foundation for learner advocacy. They allow students to articulate their learning experiences and marketable skills in meaningful ways to the external world. Over a lifetime of learning, these credentials help learners progress toward desired career outcomes while bringing visibility and advertising to institutional brands.
When institutions embed rich content into digital credentials (like student portfolios or program websites), they add context to an otherwise static market of learning credentials. Empowering learners to showcase their achievements makes prospective students feel confident about their decision to pursue education with specific providers.
How Are Leading Institutions Transforming Continuing Education?
Real-world examples demonstrate how forward-thinking institutions are successfully implementing comprehensive continuing education support for their students. These success stories illustrate practical applications of the modern student lifecycle in action.
Continuing Ed Technology Platforms
Saïd Business School at Oxford University exemplifies how prestigious institutions can leverage technology to expand their continuing education reach. By implementing tech solutions, they streamlined their non-traditional student management processes while maintaining the academic rigor that defines their brand. Their approach demonstrates how established institutions can adapt to serve adult learners without compromising their educational standards.
The school recognized that executive education and professional development programs required different operational approaches than traditional degree programs. By adopting purpose-built technology for continuing education, they could offer more flexible enrollment options, personalized learning pathways and seamless integration between online and in-person components.
Leveraging Micro-Credentials
Similarly, Metropolitan State University of Denver transformed its micro-credentials management process to better serve working professionals seeking skills-based training. Their implementation of streamlined curriculum management allowed them to rapidly develop and deploy new micro-credential programs that respond quickly to workforce demands.
MSU Denver's transformation highlights the importance of agile program development in modern continuing education. By reducing the time required to bring new programs to market, they can respond more effectively to emerging skill gaps and industry needs.
Both institutions demonstrate how technology solutions specifically designed for continuing education can transform traditional higher education operations. Institutions don't need to choose between academic excellence and operational efficiency because the right systems enable both.
What Technologies Are Reshaping Continuing Education Support?
Online learning platforms have become more sophisticated and user-friendly. Modern systems now offer features that were unimaginable just a few years ago, changing how continuing education supports students throughout their learning lifecycle.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are enabling truly personalized learning experiences. These technologies can track student performance in real time, identify knowledge gaps and recommend specific resources or interventions to keep learners on track. For continuing education students who often have limited time for coursework, personalization can make the difference between success and failure.
Mobile learning has become essential rather than optional. With 98% of Americans having smartphones, computers or tablets, mobile learning apps provide accessibility for learners who study during brief time windows throughout their day. The best continuing education platforms now offer full mobile functionality, allowing students to progress through coursework during commutes, lunch breaks or other available moments.
Hybrid continuing education models are leveraging these technological advances to create seamless experiences that blend online and in-person elements. Nearly 50% of students now prefer hybrid learning formats to fully in-person instruction, driving demand for flexible delivery options that accommodate diverse learning preferences and schedules.
How Can Institutions Implement Effective Lifecycle Support?
Implementing comprehensive lifecycle support for CE students requires strategic planning and the right technological foundation. Institutions must create integrated experiences that support students throughout their entire learning journey.
The first step involves developing a clear understanding of your learner personas and their specific needs at different career stages. Recent graduates need different support than mid-career professionals seeking advancement or experienced workers transitioning to new fields. Each group requires tailored messaging, course formats and support services.
Technology integration plays a role in scaling personalized support. Modern continuing education management systems can automate many routine tasks while providing the data insights necessary to improve student outcomes. These systems should integrate seamlessly with existing infrastructure while providing the flexibility to adapt as student needs evolve.
Staff training and organizational culture also require attention. Supporting lifelong learners demands different approaches than serving traditional students. Staff members need to understand the unique challenges faced by adult learners and be equipped with tools and processes that facilitate rather than hinder the learning experience.
FAQ
What is the difference between traditional and modern continuing education? Modern continuing education focuses on lifelong learning support through flexible delivery methods, personalized learning pathways and technology-enabled experiences, while traditional continuing education typically consisted of standalone professional development courses without ongoing student relationship management.
How do online learning platforms support career transition programs? Online learning platforms provide flexible scheduling, self-paced learning options, mobile accessibility and personalized content recommendations that accommodate working professionals seeking to develop new skills while maintaining current employment obligations.
What makes hybrid continuing education more effective than fully online or in-person options? Hybrid continuing education combines the flexibility and accessibility of online learning with the engagement and hands-on experience of in-person instruction, allowing students to choose the most appropriate format for different types of learning activities while accommodating their schedule constraints.
Lifelong Learning Is the Future
As lifelong learning becomes the norm, continuing education leaders must become comfortable with new and modular learning approaches that can be applied across different stages of the student lifecycle.
Continuing education is a core component of institutions' mission to support lifelong learning. Skills-based training, career transition programs and hybrid continuing education models are essential shifts in how education operates.
The rise of online learning platforms and the growing demand for flexible, personalized education options create opportunities for institutions willing to adapt their approaches. By implementing comprehensive student lifecycle management and leveraging technology solutions designed specifically for continuing education, institutions can build sustainable advantages while serving the evolving needs of modern learners.
The 60-year curriculum model is the future of higher education, where institutions support learners throughout their entire career journey. Modern Campus empowers institutions to attract, engage and retain learners for life with comprehensive solutions designed specifically for the modern student lifecycle. Request a demo to see how we can help enhance your approach to continuing education.
Last updated: November 12, 2025



