Microcredentials for Teachers: Trends, Benefits and Programs
Teacher specific microcredentials are revolutionizing professional development with competency-based, flexible learning that fits educators' busy schedules.
- Increases in microcredential availability demonstrate rapid adoption across educational institutions
- NEA and Digital Promise lead with teacher-specific programs focusing on practical classroom skills and pedagogical competencies
- Teachers gain stackable credentials, social media shareable badges and clear career advancement pathways with verified competencies
- Technology integration enables personalized learning, automated assessment and blockchain verification for credential authenticity
Modern institutions are implementing comprehensive microcredentialing systems to attract and retain quality educators while meeting continuing education requirements.
The teaching profession faces a crisis. With 35% of American higher education teachers reporting burnout and 8% of public school teachers leaving the profession entirely, educational leaders are desperately seeking innovative solutions to support and retain their most valuable asset: teachers. Microcredentials for teachers offer a transformative approach to professional development that's reshaping how educators learn, grow and advance their careers.
Unlike traditional professional development that often feels disconnected from classroom realities, microcredentials for teachers offer targeted, competency-based learning opportunities that directly address the skills educators need most. These digital credentials and certification pathways provide flexible, personalized development that fits into teachers' demanding schedules while delivering measurable results for both educators and their students.
Why Offer Microcredentials for Teachers?
Microcredentials shift from the traditional "sit-and-get" professional development model that has dominated education for decades. These competency-based certifications focus on specific skills and require teachers to demonstrate mastery through evidence-based assessments, practical applications and real classroom implementation.
The need for this transformation becomes clear when examining current education statistics. Seventy-four percent of districts believe coaching and mentoring are the most effective offerings for supporting teacher retention, yet traditional PD programs often lack the personalization and flexibility that modern educators require.
Teacher credentialing addresses several critical gaps in conventional professional development. First, it acknowledges that teachers have diverse learning needs based on their experience level, subject area and specific classroom challenges. Second, it provides immediate applicability. Teachers can immediately implement what they learn rather than waiting months or years to apply theoretical knowledge.
With teacher shortages affecting 74% of districts for the 2024–25 school year and replacement costs averaging $25,000usd per teacher in large districts, educational institutions need cost-effective solutions that simultaneously support existing educators while attracting new talent to the profession.
How Are Microcredentials Transforming Teacher Professional Development?
Traditional professional development has long been criticized for prioritizing attendance over actual learning outcomes. Teachers earn credits simply for showing up to workshops or completing courses, regardless of whether they've mastered new skills or can effectively apply them in their classrooms.

Microcredentials for teachers flip this paradigm. Each credential requires educators to demonstrate specific competencies through portfolios, classroom evidence, student work samples and reflective analyses. This competency-based approach ensures that teachers actively engage with content and prove they can effectively implement new strategies.
The National Education Association (NEA) has embraced this model wholeheartedly, offering over 175 microcredentials created by educators for educators. These credentials span everything from classroom management and student engagement to technology integration and social-emotional learning, providing teachers with targeted opportunities that directly address their specific needs.
Personalized Learning Paths for Diverse Teaching Roles
One of the most powerful aspects of teacher microcredentials is their ability to create personalized learning journeys. Unlike one-size-fits-all workshops, microcredentials allow educators to choose professional development based on their individual goals, skill gaps and student needs.
A high school science teacher struggling with student engagement might pursue microcredentials in gamification and project-based learning, while an elementary educator could focus on social-emotional learning and differentiated instruction. This targeted approach ensures that professional development time, often limited and precious for busy teachers, is spent on skills that will have immediate classroom impact.
Digital Promise, a leader in the educator microcredential ecosystem, has developed a comprehensive framework that emphasizes this personalization. Their platform allows teachers to explore various pathways, stack credentials toward larger certifications and build expertise progressively over time.
Integration with State Licensing and Continuing Education Requirements
Perhaps most importantly for teacher retention and career advancement, microcredentials are gaining recognition within formal education systems. Thirty-one states currently allow teachers to count microcredentials toward continuing education in some capacity, with more states exploring similar policies.
Rather than requiring teachers to complete arbitrary credit hours, states and districts are beginning to recognize competency-based learning that directly improves classroom practice.
The Washington Education Association, for example, has developed a comprehensive support structure that allows teachers to earn state clock hours for completing NEA microcredentials. This recognition validates the rigor and relevance of microcredential programs while providing teachers with tangible career benefits for their professional growth efforts.
Key Benefits of Teacher microcredentials
The advantages of microcredentials for teachers surpass simple professional development. Here are the most significant benefits transforming how educators approach their professional growth:
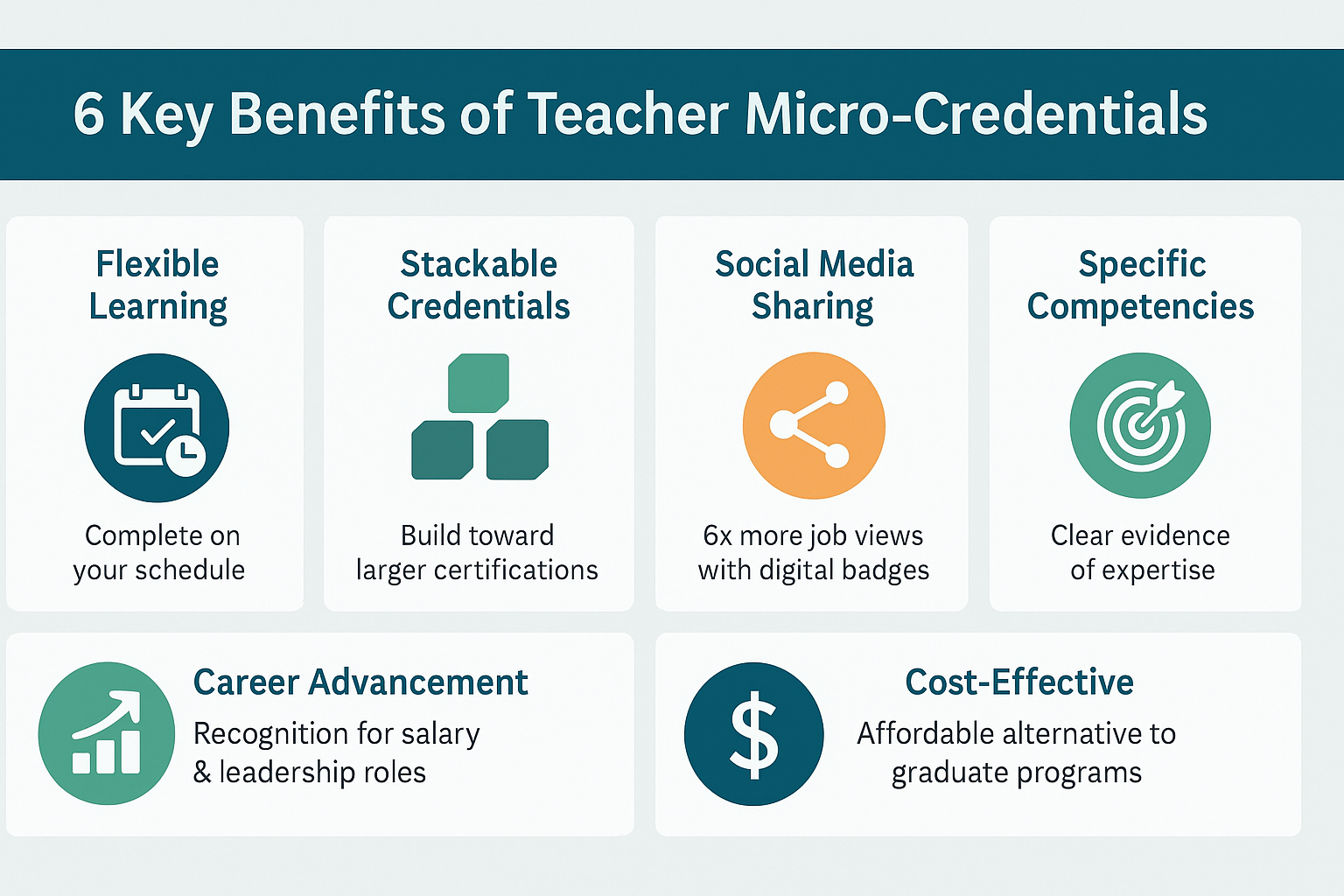
1. Flexible, Self-Paced Learning
Teachers can complete microcredentials on their own schedule, studying during summer breaks, evenings or whenever time permits. Flexibility is crucial for educators who often work long hours and have limited time for professional development during the school year.
2. Stackable Credentials Toward Larger Certifications
Many microcredential programs allow teachers to combine individual credentials into larger certifications or degree programs. This stackable approach provides clear pathways for career advancement without requiring massive upfront time investments.
3. Social Media Shareable Digital Badges
Digital badges make professional accomplishments visible and verifiable across social media platforms and professional networks. Individuals with digital credentials get viewed six times more than those without during job hunts, giving teachers a competitive advantage in the employment market.
4. Clear Evidence of Specific Competencies
Unlike traditional transcripts that list course titles and grades, microcredentials provide detailed information about exactly what skills a teacher has mastered. Employers and administrators can quickly understand a candidate's specific expertise areas.
5. Career Advancement Opportunities
Many districts are beginning to recognize microcredentials for salary advancement, leadership roles and specialized positions. Teachers with relevant microcredentials often have advantages when applying for instructional coaching roles, department leadership positions or technology integration specialists.
6. Cost-Effective Alternative to Graduate Programs
While master's degrees can cost tens of thousands of dollars, microcredentials typically cost hundreds or even less. Affordability makes professional development accessible to teachers regardless of their financial situation, democratizing access to high-quality learning opportunities.

Which Organizations Lead Teacher microcredentialing Programs?
NEA's 175+ Educator-Created microcredentials
The National Education Association is the largest provider of teacher-specific microcredentials in the United States. All credentials are created by practicing educators, content is grounded in research and best practice, and the platform offers incredible diversity in topic areas.
NEA microcredentials cover everything from climate justice and effective teacher-paraeducator teams to classroom management and social-emotional learning. Each credential requires teachers to submit evidence of their learning and implementation, ensuring that professional development translates into improved classroom practice.
Digital Promise's Competency-Based Framework
Digital Promise has pioneered the educator microcredential ecosystem through its comprehensive platform and research initiatives. Their approach emphasizes competency-based assessment, peer review and continuous improvement of credential offerings.
What sets Digital Promise apart is its commitment to research and evaluation. They regularly publish studies on microcredential effectiveness, educator satisfaction and impact on student outcomes, providing evidence-based support for the microcredentialing movement.
State-Level Implementation Examples
Several states have developed their own microcredential programs tailored to local education priorities. New Mexico's Advancement Program Level (APL) microcredentials support teachers advancing from Level 1 to Level 2 and Level 2 to Level 3 licensure through competency-based stacked courses.
Arizona’s Teachers Academy offers microcredentials designed to support educators in meeting state-specific instructional goals. These stackable credentials focus on high-need areas such as classroom management, culturally responsive teaching and student engagement, helping teachers enhance their practice while working toward certification or advanced career opportunities.
State programs often align with specific evaluation systems and career advancement pathways, providing teachers with clear connections between professional development and career growth opportunities.
How Do Digital Badges Enhance Teacher Credentialing?
Blockchain Verification and Security
Modern digital badge systems employ blockchain technology to ensure credential authenticity and prevent fraud. Security is crucial as microcredentials become more valuable in the job market and for career advancement.
Each digital badge contains metadata that details the criteria for earning the credential, evidence required and the issuing organization. Transparency allows employers and administrators to quickly verify the rigor and relevance of a teacher's professional development.
Social Media Integration and Marketing Impact
Digital badges transform teachers from consumers into marketers for their institutions and programs. When educators share their accomplishments on social media platforms, they create authentic testimonials for the credentialing programs.
Organic marketing can boost web traffic up to 15 times to program pages, creating a powerful recruitment tool for institutions offering microcredentials. The viral nature of social media sharing helps expand awareness of opportunities to educators who might not otherwise discover them.
Data Analytics for Program Improvement
Digital badge platforms provide unprecedented insights into how teachers engage with professional development. Analytics can reveal which credentials are most popular, completion rates, time to completion and correlation with other educational outcomes.
This data enables program administrators to continuously improve their offerings, identify gaps in professional development needs and develop new credentials that address emerging educational challenges.
What Technology Trends Are Shaping Teacher microcredentials?
AI-Powered Personalization
Artificial intelligence is beginning to transform how teachers discover and engage with microcredential opportunities. AI systems can analyze a teacher's background, interests and professional goals to recommend specific credentials that align with their career development needs.
Personalized learning pathways become increasingly sophisticated as AI learns from teacher behavior and outcomes, creating customized professional development journeys that maximize relevance and impact.
Learning Management System Integration
Modern microcredential platforms integrate with existing learning management systems, making it easier for teachers to access professional development within familiar digital environments. Integration reduces barriers to participation and creates more cohesive learning experiences.
Mobile-First Design for Busy Educators
Recognizing that teachers often have limited time at desktop computers, leading microcredential platforms prioritize mobile-friendly design. Teachers can complete coursework, submit evidence and track progress from their smartphones or tablets, fitting professional development into brief windows of available time.
How Can Institutions Implement Successful Teacher Microcredentialing Programs?
Policy and Administrative Considerations
Successful implementation requires clear policies that define how microcredentials align with existing professional development requirements, salary advancement and career pathways. Administrators must work with teacher unions and state education departments to ensure proper recognition and integration.
Meaningful credential pathways require alignment between institutional priorities, teacher needs and student outcomes. This alignment ensures that microcredentials contribute to broader educational goals rather than simply adding to teachers' workload.
Technology Infrastructure Requirements
Implementing microcredentials requires a robust technology infrastructure capable of supporting digital badge creation, assessment management and analytics. Institutions must consider integration with existing systems, security requirements and scalability for future growth.
Faculty Buy-In and Change Management
Successful microcredential programs require strong faculty support and effective change management strategies. Teachers need to understand the benefits of competency-based professional development and feel confident that their additional efforts will be recognized and rewarded.
Microcredentials help educators understand how to create evidence portfolios, navigate digital platforms and maximize the career benefits of their achievements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to earn a teacher microcredential? Most teacher microcredentials require a manageable time commitment and can be completed over several weeks or months, depending on the educator’s schedule. Their self-paced structure allows teachers to work through the material during summers, breaks or whenever time permits.
Do microcredentials count toward continuing education requirements? Yes, several states currently allow teachers to count microcredentials toward their continuing education requirements, with more states developing similar policies. Teachers should check with their state education department and local district for specific recognition policies.
What's the difference between digital badges and microcredentials? Digital badges are the visual representation of microcredentials, essentially the "certificate" that displays achievement. Microcredentials are the actual competency-based learning experiences that teachers complete to earn the badge. All microcredentials result in digital badges, but not all digital badges represent full microcredentials.
Empower Educators and Elevate Outcomes with Microcredentials for Teachers
The transformation of teacher professional development through microcredentials is a fundamental reimagining of how we support educator growth and career advancement. As the education sector continues to grapple with retention challenges and evolving student needs, microcredentials for teachers offer a flexible, personalized and effective solution that benefits educators, institutions and students.
The success stories emerging from organizations like NEA, Digital Promise and state-level implementations demonstrate that when properly designed and supported, teacher microcredentials can significantly improve educator satisfaction, skill development and career outcomes. The integration of digital badges, competency-based assessment and personalized learning pathways creates experiences that respect teachers' time while delivering measurable results.
Modern Campus helps institutions implement comprehensive microcredentialing systems that support teacher growth while driving institutional success in the evolving landscape of education. Request a demo to see how microcredentials can be a powerful tool for creating a more engaged, skilled and satisfied educator workforce.
Last updated: August 15, 2025




